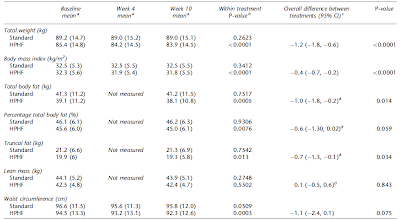
Further Evidence: High Protein Diet Conserves Lean Mass
It is becoming common knowledge that consuming a diet (relatively) high in proteins conserves muscle mass. Thus, a recent study by Case & Haub ( Case. 2010 ) only confirms what regular visitors of the SuppVersity obviously knew. The scientists investigated the effect of either a high carbohydrate (CHO; 65% carbohydrates, 15% protein and 20% fats), a "high protein" (PRO; 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein and 30%) and a non-restricted (Control) diet on body composition and weight of 30 active, military males (age=25 ± 4 yr, body fat=15 ± 7%): Control and PRO group increased FFM , 1.7±1.2 kg and 0.8±1.5 kg, respectively. CHO group lost -0.2±3.8 kg FFM. PRO and CHO groups lost 1.0±1.0 kg and 1.0±1.8 kg of FM, respectively. Control group lost 0.7±0.7 kg FM. Although, judged by a bodybuilders standard, for example, the "PRO"-Diet was not really "high protein" in the sense that it still had 40% carbs and thus more carbs than protein, it was exceptionall...