Want to Increase Your Testosterone? Better Have Your Right Answers
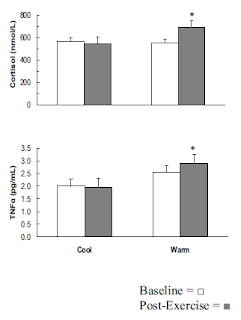
Although this is not a typical SuppVersity-study, it is yet related to both education and endocrinology: Flegr and Priplotova from the Charles University in Praha found that testosterone and cortisol levels in university students reflect actual rather than estimated number of wrong answers on written exam ( Flegr. 2010 ). The scientists measured testosterone and cortisol levels in response to a written exam in students of the undergraduate biology program of their university. The results were surprising: "The number of wrong answers was a better predictor of the hormonal changes (increase in successful, decrease in unsuccessful students) than the self-estimated number of wrong answers or a subjectively opinionated impression from the exam." ( Flegr. 2010 ) So, while high testosterone to cortisol ratios before the exams did correlate negatively with self-estimated number of wrong answers, the bodies of the subjects reacted to what I suspect was an increased feeling of distres...