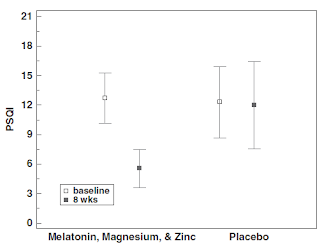
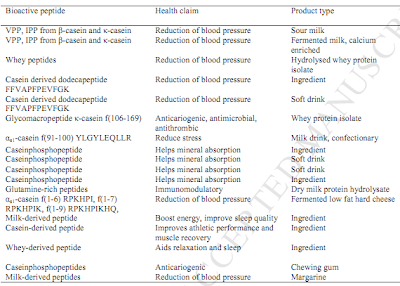
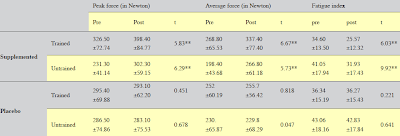
Resveratrol Increases Lipolysis and Reduces Lipogenesis in Mature Adipocytes
If you are (as I hope) an avid reader and daily visitor of the SuppVersity, you probably remember Friday's news on the " Side Effects of Polyphenol Supplementation ". I just hope you did not throw away all your supplements immediately, because eventually the question of side effects is always relative. If, for example, you are a sumo competitor and in dire need of gaining mass, no matter what. It would be an unwelcome side-effect of resveratrol supplementation not to gain or even to lose body fat... A report ( Baile. 2011 ), recently published in the Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences does now confirm, what supplement companies have been promising all along: the right dose of supplemental resveratrol will limit fat gain and improve lipolysis in a mouse model: Treatment of mice with resveratrol alone was shown to improve resistance to weight gain caused by a high-fat diet. Moreover, dietary supplementation of aged ovariectomized rats with a combination o...