Soccer Molecule of Youth? Fullerene C60 Increases Lifespan by +90% and Protects Against Free Radicals
 |
| Image 1: Fullerenes are carbon molecules with a specific symmetrical structure; the Buckminster fullerene C60, for example, which is made of 20 hexagons and 12 pentagons, with a carbon atom at the vertices of each polygon and a bond along each polygon edge looks like a soccer ball (img. Bryn C.) |
The earliest studies on the biological and pharmacological properties of [60]fullerene, as the "correct" notation for the "soccer ball-ish" Buckminster fullerene would be, date back to the early 1990. Despite its established usefulness in DNA cleavage, imaging, UV and radioprotection, as well as its antiviral, antioxidant, and anti-amyloid (=anti Alzheimer's) activities, its ameliorative effect on allergic response and its inhibitory effects on angiogenesis and tumor growth, very little is known about its pharmacology and long(er) term safety, the primary research interests of the French and Tunesian scientists whose recently published paper attracted my attention (Moussa. 2012).
Want to know more about C60? How it works? How this study relates to the Free Radical Theory of Aging and if anti-oxidants are actually good for you? In that case, you should listen to my interview on Carl Lanore's Super Human Radio, which aired on Thursday, April 19th, 2012 (click here to dowload the MP3 file).
Put some "soccer balls" in your olive oil and live into your late 150s
Since study was designed as a general investigation - not as a test for the longevity effects of the "soccer fullerene" - the actual study consisted of a couple of experiments designed to...
- test the preparation technique - 50mg of C60 dissolved in 10ml of virgine olive oil
- pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies - after oral and intra-peritoneal administration
- chronic toxicity effects - 0.8mg C60 every day for the 1st week, then weekly until the end of the 2nd month, then every two weeks until the end of the 7th month
- anti-oxidant effects - 0.8mg C60 pre-treatment for 7 days before administration of a single dose of CCl4 (1ml/kg bw) as an oxidative stressor
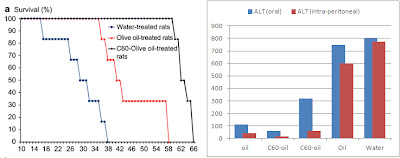 |
| Figure 1: Estimated median life-span of healthy rats (left) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT; liver enzyme) values of control (oil, C60+oil) and CCl4-intoxicated (C60+oil, oil, water) rats (data adapted from Moussa. 2012) |
 |
| Figure 2: Oxidized to total glutathione ratio (GSSG/TGSG, left) and images of the livers of the rodents that were pre-treated with olive oil or olive oil + C60 (control) for seven days before administration of a hepatoxic dose (1ml/kg body weight) CCl4 (data adapted from Moussa. 2012) |
[t]he number of necrotic areas observed in the liver sections of [intra-peritoneally treated, i.p.] animals was significantly lower than that observed in the [orally treated animals]. As C60Moreover, the prevention of GSH depletion in the absence of insignificant changes in hepatic CYP2E1 activity, the reduction of which would reduce the occurrence of reactive CCl4 metabolites and thusly evidence only drug-specific, yet not general protective effects of C60, suggest that C60 exerts it hepato-protective and longevity effects via a free-radical scavenging mechanism.
concentrations in the livers of [i.p. treated] animals are probably about 10 times higher than those of the livers of [orally treated animals], these results confirm the dose effect relationship
reported previously (Gharbi. 2005).
Promising, if not exciting, but not yet market-ready
[t]hese results obtained with a small sample of animals with an exploratory protocol ask for a more extensive studies to optimize the intestinal absorption of C60 as well as the different parameters of the administration protocol: dose, posology [determination of appropriate dosages], and treatment duration.Specifically with respect to the increased life-expectancy, it must also be stressed that the treatment was stopped after 17 months and the EML, i.e. the estimated median lifespans, as well as the corresponding figure +90% are statistical numbers -- just as the COX hazard ratios in other studies are, by the way. So no reason to start crying "fraud", especially if you also take into account the established health-benefits (anti-cancer, anti-heart disease, anti-Alzheimer's ,etc.) that will come from the reduced oxidation alone. The only 'downside' therefore seem to be that we would probably have to cope with a whole new problem soon after C60 hits the over-the-counter marked: I mean, what do we do with all the 150y+ old-age pensioners on C60?



