Yohimbine as an Ergogenic? 5mg of Yohimbine 2h Before Cycling to Exhaustion Increase Time to Exhaustion by 29%, Energy Expenditure & Fatty Acid Oxidation by >10%
 |
| Many people take yohimbine before cycling, but few know that it's not just increasing fat loss, but also their cycling performance on the bike. |
A recent study from the Al-Mustansiriya and Kabala Universities did yet find that "yohimbine accelerates and improves cycling performances via positive ergogenic effects" (Al-Kuraishy. 2014). If this is actually true, the authors, Al-Kuraishy and Abood, would in fact be right to say that "yohimbine can be used as ergogenic agent for ameliorating the physical fatigue" (Al-Kuraishy. 2014).
In the subsequent non-blinded test with yohimibine, the subjects took a sinlge 5 mg yohimbine tablet (orally) 2h before they jumped onto the bike again, where they performed another standardized cycling ergometer test to fatigue state.
Moreover, the authors found that yohimbine significantly accelerated the oxygen consumption at the "fat burning" and maximal intensities and the maximal and resting heart rate of the subjects (p < 0.05 | Figure 2).
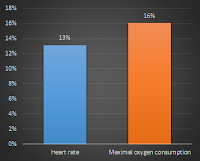 |
| Figure 2: Increase in heart rate and maximal oxygen consumption (indicative of increased fatty acid oxidation) with yohimbine relative to control (Al-Kuraishy. 2014). |
Since it is however unlikely that you would see a 29% increase in time to exhaustion and significant increases in fat oxidation as they are indicated by the increase in VO2 consumption (Figure 2) being triggered by placebo, we can probably assume that yohimbine is not only a fat burner, but also an endurance supplement that works - most probably - by increasing the consumption of fatty acids and decreasing the reliance on glycogen + little researched effects on the brain (Hagan. 1986; Yan. 1993) | Comment on Facebook!
- Al-Kuraishy, Hayder M., Haidar AN Abood, and Ali Ismail A. Al-Gareeb. "Ergogenic Effects of Yohimbine: Standardized Cycling Clinical Study." Karbala J. Med. Vol.7, No.2, Dec, 2014
- Hagan, R. M., and I. E. Hughes. "Yohimbine affects the evoked overflow of neurotransmitters from rat brain slices by more than one mechanism." Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 38.3 (1986): 195-200.
- Yan, Qing-Shan, Philip C. Jobe, and John W. Dailey. "Noradrenergic mechanisms for the anticonvulsant effects of desipramine and yohimbine in genetically epilepsy-prone rats: studies with microdialysis." Brain research 610.1 (1993): 24-31.









